Blue Dot Technology
Conductive vs. Hi-Strength Retaining Nuts
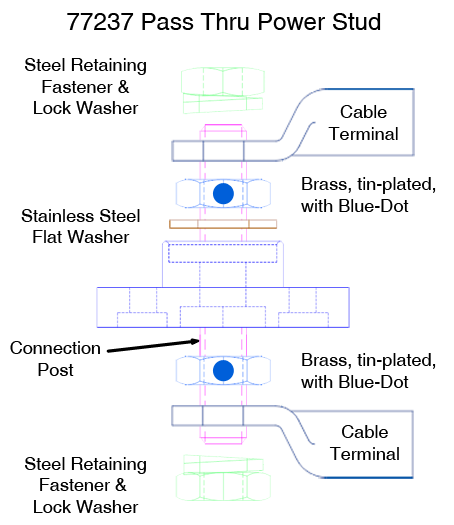
VTE Inc. uses two type of retaining fasteners:
- Conductive Fasteners
- Mechanical Fasteners
Conductive Fasteners
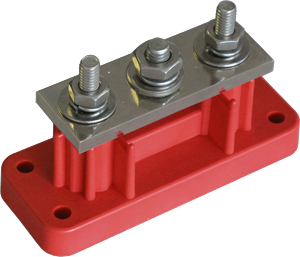
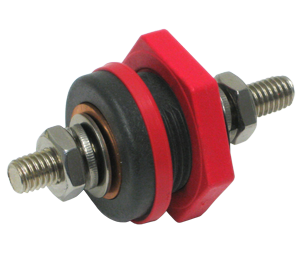
Our conductive fasteners are used where current will pass through the fastener. The electrical properties are such that conductivity is superior to mechanical fasteners.
- - Brass conductivity: 37%
- - Stainless steel conductivity: 2.4%
Mechanical Fasteners
Our retaining fasteners are used where current does not need to pass through the fastener. An example of this would be at the end of a connection post, to tighten an assembly.
Some key points:
- Conductive nuts include: brass, tin-plated brass. On some bus material: nickel-plated brass. Brass is used for its superior conductivity to stainless steel.
- Mechanical nuts: stainless steel, steel. Steel is used to tighten, or torque an assembly. Steel is much harder, and can handle higher torque before distortion.
- Brass and copper are more expensive than steel, and are only used where conductivity is required.
- Brass (or plated) nuts are marked by VTE with a Blue Mark. This is to notify the installer that the fastener is for conductivity positions only.
- Conductivity nuts are installed by the factory, and must be left in their original position.
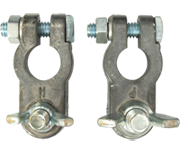
- When installing multiple lug or ring terminals, washers are not recommended between terminals.

 United States
United States